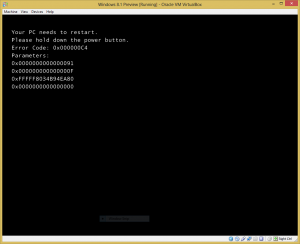
Updating Oracle Linux installations via the Oracle public yum server has been cumbersome because the download speeds I have been getting are quite terrible.
Having quite a number of Oracle Linux installations compounds the issue as each server will have to endure the same slow download speeds for the same packages. One way to stop this from happening is having a local mirror of the public yum server. This local mirror will perform the download of the packages from the public yum server, and all other Oracle Linux installations will then grab the packages from the local mirror, saving lots of time.
I have been scouring the internet for days looking for the best way to do this, and I think the best guide so far comes from this post by Martin Nash.
I hope to setup my own mirror soon.
Update 19 August 2013
Below are the steps to setup yum mirror from a fresh CentOS 6.4 Minimal Install.
Create the directory to put the repository in.
# mkdir -p /repos/x86_64
Install the yum-utils and createrepo packages that provide the reposync and createrepo commands.
# yum install yum-utils createrepo
Set up the repository to mirror as per the instruction at Oracle. Open the repo file and disable all repos by making sure enabled=0 for all repos.
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/public-yum-ol6.repo
Run reposync. This will take quite a long time, especially with the slow speeds from the Oracle public yum server.
# reposync --repoid=ol6-latest --repoid=ol6-UEK-latest -p /repos/ol6
After the reposync command finished downloading all the packages from the source repo, run createrepo to create the repository metadata.
# createrepo /repos/ol6/ol6_UEK_latest/getPackage/
# createrepo /repos/ol6/ol6_latest/getPackage/
Create a script to re-run the above as often as required (I am going to run it once a day).
#!/bin/bash
LOG_FILE=/repos/logs/orayum-update_$(date +%Y.%m.%d).log
/usr/bin/reposync --repoid=ol6_latest --repoid=ol6_UEK_latest -p /repos/ol6 >> $LOG_FILE 2>&1
/usr/bin/createrepo /repos/ol6/ol6_UEK_latest/getPackage/ >> $LOG_FILE 2>&1
/usr/bin/createrepo /repos/ol6/ol6_latest/getPackage/ >> $LOG_FILE 2>&1
Create the directories to store the script and logs, and move the script inside the directory
# mkdir -p /repos/logs
# mkdir -p /repos/scripts
# mv orayum-update.sh /repos/scripts
Make the script executable
# chmod +x /repos/scripts/orayum-update.sh
Add the script to crontab, and run once every day.
# crontab -e
0 0 * * * /repos/scripts/orayum-update.sh
# crontab -l
0 0 * * * /repos/scripts/orayum-update.sh
Install and configure Apache webserver.
# yum install httpd
# chkconfig httpd on
# service httpd start
Now configure Apache to serve the repository.
# mkdir -p /var/www/html/repo/OracleLinux/OL6/latest
# mkdir -p /var/www/html/repo/OracleLinux/OL6/UEK/latest
# ln -s /repos/ol6/ol6_latest/getPackage/ /var/www/html/repo/OracleLinux/OL6/latest/x86_64
# ln -s /repos/ol6/ol6_UEK_latest/getPackage/ /var/www/html/repo/OracleLinux/OL6/UEK/latest/x86_64
Open up the firewall for Apache.
# iptables -I INPUT 5 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT
# service iptables save
Now we need to fix the SELinux contexts for the repository files, so that the repository, which is soft-linked from the /var/www/html sub-folders, can be served by Apache.
# yum install policycoreutils-python
# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "/repos/ol6/ol6_latest/getPackage(/.*)?"
# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "/repos/ol6/ol6_UEK_latest/getPackage(/.*)?"
# restorecon -R -v /repos/ol6/
Get the repository GPG key as well, and put it into the root Apache directory.
# cd /var/www/html
# wget http://public-yum.oracle.com/RPM-GPG-KEY-oracle-ol6
Now the local yum mirror is fully setup! Local Oracle Linux 6 installations can now use this repository by creating a repo file in /etc/yum.repos.d/ folder.
# cd /etc/yum.repos.d
# vi public-yum-ol6-local.repo
The repo file looks something like this:
[ol6_latest_local]
name=Oracle Linux $releasever Latest ($basearch)
baseurl=http://<hostname>/repo/OracleLinux/OL6/latest/$basearch/
gpgkey=http://<hostname>/RPM-GPG-KEY-oracle-ol6
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
[ol6_UEK_latest_local]
name=Latest Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel for Oracle Linux $releasever ($basearch)
baseurl=http://<hostname>/repo/OracleLinux/OL6/UEK/latest/$basearch/
gpgkey=http://<hostname>/RPM-GPG-KEY-oracle-ol6
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
Done!